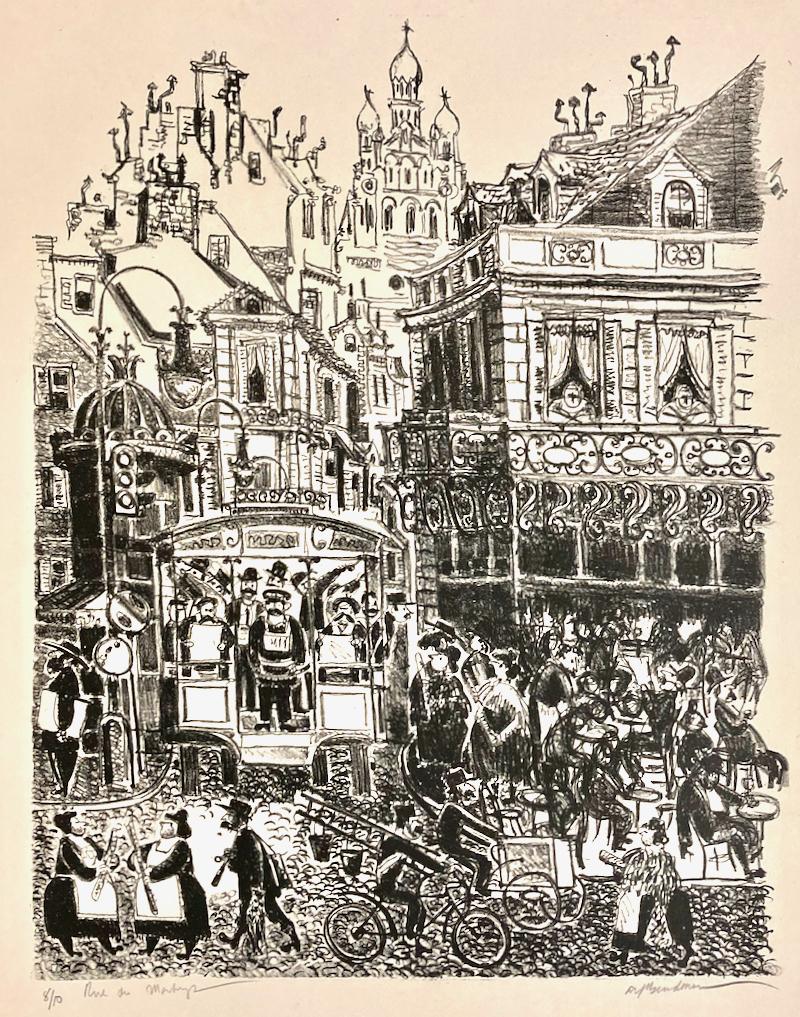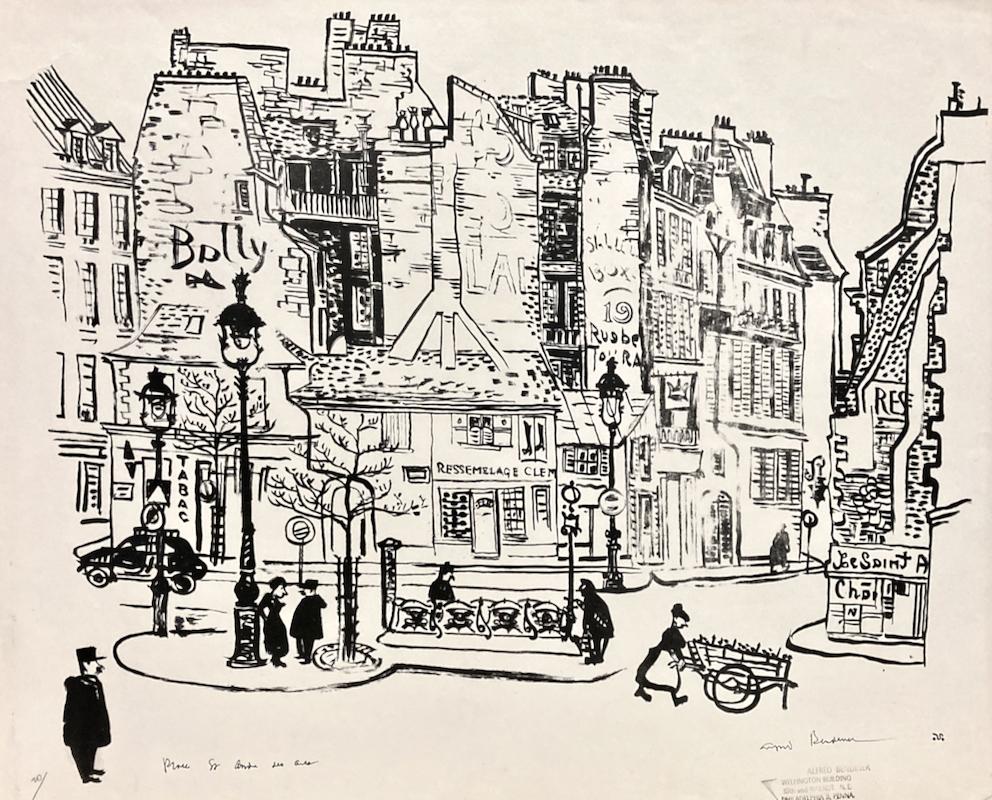Items Similar to New York Night
Want more images or videos?
Request additional images or videos from the seller
1 of 10
Adolf DehnNew York Night1930
1930
About the Item
New York Night\Lithograph, 1930
Edition: 30
Printer: Meister Schulz, Berlin
Printed on heavy wove paper without watermark
This lithograph was created in Berlin from Dehn's vivid memories of the Metropolis. This image depicts the monumental scale of the New York City skyline and the movement and commotion on the street below.
Provenance: Estate of the artist
Virginia Dehn (the artist's widow)
Dehn Quest
Reference: Lumsdaine & O'Sullivan 182
Illustrated: Adams, The Sensuous Life of Adolf Dehn, Fig. 9.13, page 212
Adolf Dehn, American Watercolorist and Printmaker, 1895-1968
Adolf Dehn was an artist who achieved extraordinary artistic heights, but in a very particular artistic sphere—not so much in oil painting as in watercolor and lithography. Long recognized as a master by serious print collectors, he is gradually gaining recognition as a notable and influential figure in the overall history of American art.
In the 19th century, with the invention of the rotary press, which made possible enormous print runs, and the development of the popular, mass-market magazines, newspaper and magazine illustration developed into an artistic realm of its own, often surprisingly divorced from the world of museums and art exhibitions, and today remains surprisingly overlooked by most art historians. Dehn in many regards was an outgrowth of this world, although in an unusual way, since as a young man he produced most of his illustrative work not for popular magazines, such as The Saturday Evening Post, but rather for radical journals, such as The Masses or The Liberator, or artistic “little magazines” such as The Dial. This background established the foundation of his outlook, and led later to his unique and distinctive contribution to American graphic art.
If there’s a distinctive quality to his work, it was his skill in introducing unusual tonal and textural effects into his work, particularly in printmaking but also in watercolor. Jackson Pollock seems to have been one of many notable artists who were influenced by his techniques.
Early Years, 1895-1922
For an artist largely remembered for scenes of Vienna and Paris, Adolf Dehn’s background was a surprising one. Born in Waterville, Minnesota, on November 22, 1895, Dehn was the descendent of farmers who had emigrated from Germany and homesteaded in the region, initially in a one-room log cabin with a dirt floor. Adolf’s father, Arthur Clark Dehn, was a hunter and trapper who took pride that he had no boss but himself, and who had little use for art. Indeed, during Adolf’s boyhood the walls of his bedroom and the space under his bed were filled with the pelts of mink, muskrats and skunks that his father had killed, skinned and stretched on drying boards. It was Adolf’s mother, Emilie Haas Dehn, a faithful member of the German Lutheran Evangelical Church, who encouraged his interest in art, which became apparent early in childhood. Both parents were ardent socialists, and supporters of Eugene Debs. In many ways Dehn’s later artistic achievement was clearly a reaction against the grinding rural poverty of his childhood.
After graduating from high school in 1914 at the age of 19—an age not unusual in farming communities at the time, where school attendance was often irregular—Dehn attended the Minneapolis School of Art from 1914 to 1917, whose character followed strongly reflected that of its director, Munich-trained Robert Kohler, an artistic conservative but a social radical. There Dehn joined a group of students who went on to nationally significant careers, including Wanda Gag (later author of best-selling children’s books); John Flanagan (a sculptor notable for his use of direct carving) Harry Gottlieb (a notable social realist and member of the Woodstock Art Colony), Elizabeth Olds (a printmaker and administrator for the WPA), Arnold Blanch (landscape, still-life and figure painter, and member of the Woodstock group), Lucille Lunquist, later Lucille Blanch (also a gifted painter and founder of the Woodstock art colony), and Johan Egilrud (who stayed in Minneapolis and became a journalist and poet).
Adolf became particularly close to Wanda Gag (1893-1946), with whom he established an intense but platonic relationship. Two years older than he, Gag was the daughter of a Bohemian artist and decorator, Anton Gag, who had died in 1908. After her husband died, Wanda’s mother, Lizzi Gag, became a helpless invalid, so Wanda was entrusted with the task of raising and financially supporting her six younger siblings. This endowed her with toughness and an independent streak, but nonetheless, when she met Dehn, Wanda was Victorian and conventional in her artistic taste and social values. Dehn was more socially radical, and introduced her to radical ideas about politics and free love, as well as to socialist publications such as The Masses and The Appeal to Reason.
Never very interested in oil painting, in Minneapolis Dehn focused on caricature and illustration--often of a humorous or politically radical character. In 1917 both Dehn and Wanda won scholarships to attend the Art Students League, and consequently, in the fall of that year both moved to New York. Dehn’s art education, however, ended in the summer of 1918, shortly after the United States entered World War I, when he was drafted to serve in the U. S. Army. Unwilling to fight, he applied for status as a conscientious objector, but was first imprisoned, then segregated in semi-imprisonment with other Pacifists, until the war ended. The abuse he suffered at this time may well explain his later withdrawal from taking political stands or making art of an overtly political nature. After his release from the army, Dehn returned to New York where he fell under the spell of the radical cartoonist Boardman Robinson and produced his first lithographs. He also finally consummated his sexual relationship with Wanda Gag.
The Years in Europe: 1922-1929
In September of 1921, however, he abruptly departed for Europe, arriving in Paris and then moving on to Vienna. There in the winter of 1922 he fell in love with a Russian dancer, Mura Zipperovitch, ending his seven-year relationship with Wanda Gag. He and Mura were married in 1926. It was also in Vienna that he produced his first notable artistic work.
Influenced by European artists such as Jules Pascin and Georg Grosz, Dehn began producing drawings of people in cafes, streets, and parks, which while mostly executed in his studio, were based on spontaneous life studies and have an expressive, sometimes almost childishly wandering quality of line. The mixture of sophistication and naiveté in these drawings was new to American audiences, as was the raciness of their subject matter, which often featured pleasure-seekers, prostitutes or scenes of sexual dalliance, presented with a strong element of caricature. Some of these drawings contain an element of social criticism, reminiscent of that found in the work of George Grosz, although Dehn’s work tended to focus on humorous commentary rather than savagely attacking his subjects or making a partisan political statement. Many Americans, including some who had originally been supporters of Dehn such as Boardman Robinson, were shocked by these European drawings, although George Grocz (who became a friend of the artist in this period) admired them, and recognized that Dehn could also bring a new vision to America subject matter. As he told Dehn: “You will do things in America which haven’t been done, which need to be done, which only you can do—as far at least as I know America.”
A key factor in Dehn’s artistic evolution at this time was his association with Scofield Thayer, the publisher of the most notable modernist art and poetry magazine of the period, The Dial. Thayer was in Vienna being analyzed by Freud, and hired Dehn to serve as his secretary and assistant, and to supervise a portfolio of reproductions of modern art—a project which gave Dehn the equivalent of an advanced graduate tutorial in the most advanced modern art being produced in Europe at that time. Among his friends at this time was the poet and painter e. e. cummings—a Harvard classmate of Thayer.
Dehn also produced lithographs, starting in 1922, working both with a virtuosos Berlin printmaker, Meister Schulz, and a Parisian master printer, Desjobert. It was in this field that he produced arguably the most influential work of his career—lithographs in which he moved away from simply drawing with a sharp crayon and introduced a variety of unusual textural effects, such as scrubbing erasing, and scraping, with a variety of tools ranging from razor blades to sandpaper, as well as the use of washes and ink wash (known as tusche) to create effects of overall tone. As Dehn himself later replained:
When I started drawing on stone, there was one traditional way of making a lithograph. It was the approach of the purist. Neatness and the smooth surface were the highest virtues. The student was cautioned, “Don’t do this, don’t do that,” The only thing one was allowed to do was to sharpen the crayon, preferably a hard one, to the finest possible point and then stroke the one for days on end until a clean little design had been developed. It is of course evident that beautiful and great prints can be made in this manner, but this delicate and careful way o drawing was stifling for some of us. It killed the creative impulse, deadened the hand.
Dehn’s innovations had very widespread influence, and ultimately reshaped the entire character of American printmaking, producing prints that had the tonal and textural richness of a painting. In June 1937, for example, in an article in The London Studio, the virtuoso lithographer Stow Wengenroth concluded a description of a group of notable lithographs with a print by Dehn which he singled out a “The most complicated of the techniques her illustrated… Precisely the order in which the various parts were done would be hard to say.”
Dehn lived principally in Vienna from 1922 to 1926, at which point his principal residence became Paris, although in this period he was rather peripatetic, and also lived for significant periods of time in Berlin and London. During the late twenties, Dehn held regular shows of his work at the Weyhe Gallery, managed by Carl Zigrosser, which did a great deal to establish his reputation as a leading American printmaker and were also modestly successful from the financial standpoint.
The Difficult Years: 1929-1936
After the financial crash of 1929, however, sales of his prints dropped significantly, and in 1933 Zigrosser declined to stage an exhibition of his most recent prints, regarding it as not worth doing from a business standpoint. For the next few years, Dehn scrambled to earn enough to survive, often spent the summer staying with his parents in Minnesota to save money on rent, and took part in a number of unprofitable business ventures, including the short-lived Adolf Dehn Print Club. For a time he even worked for the WPA at a salary of $34 a week. Around 1932-33 his marriage to Mura Zipperovitch came to an end, and for the next three summers he carried on a romance on Martha’s Vineyard with a poet named Eileen Lake. Interestingly, Jackson Pollock was also staying nearby on Martha’s Vineyard at this time, and seems to have been influenced at this time by Dehn’s innovations in printmaking, particularly his rich textural effects.
1936-1943: Watercolor and the American Scene
Around 1936, however, he began to rebuild his career. That year he travelled to Vienna, to supervise trial-proofs of reproductions of American paintings, and then spent a few weeks traveling along the Dalmatian coast and visiting Venice and Paris. On the return voyage he did something he had thought about for years but never carried through: he took up watercolor. Remarkably, up to this point in his career--he was forty-two—aside from a few pastels, he had never worked in color. From the first, he used the medium in a way which created rich textural effects, in a fashion very unusual for the period—for example, working on water-soaked paper, or creating contrasts between transparent and opaque pigment. From the first his watercolors sold readily and received enthusiastic critical acclaim. Indeed, in his book American Watercolor and Winslow Homer, the noted scholar and museum curator Lloyd Goodrich ranked Dehn as one of the half-dozen most significant American watercolorists—as a peer of such masters as Winslow Homer, Maurice Prendergast, John Marin and Edward Hopper.
In addition, in 1938 he began producing lithographs for Associated American Artists, a print-making venture established by a marketing genius, Reeves Lowenthal, who advertised his wares in national magazines and sold them in department stores. This venture also resulted in a steady stream of income. By this time, he had a new girlfriend, Elizabeth Timmerman, who was both an actress and a photographer for Life magazine. In 1940 he received a Guggenheim grant which enabled him to take a long sketching trip around the United States, and this resulted in both a sell-out exhibition at Associated American Artists, and an article of August 11, 1941 in Life magazine, which had a circulation of millions, and brought him instant fame. At this point the American Scene movement, led by figures such as Grant Wood and Thomas Hart Benton, was getting national attention. Dehn’s work fit squarely into this new artistic tendency.
An interesting outgrowth of this trip was that Dehn visited the Colorado Springs Fine Arts Center in Colorado Springs, where his former mentor, Boardman Robinson, had become head of the art school. For the next several summers he returned to Colorado Springs, to teach. An outgrowth of this activity was a major group of landscape lithographs, produced with Lawrence Barrett, who had established a lithography studio at the school, as well as his most important book illustrations, for an edition of the stories of Guy de Maupassant. He and Barrett also co-authored a textbook on lithography, How to Draw and Print Lithographs, which was published by the American Artists Group in 1950. When World War II broke out, Dehn was too old to join the army, but supported the war effort through a series of war-related projects, engineered by Reeves Lowenthal, including one documenting Navy Blimps and another celebrating the huge oil refineries at Baton Rouge.
The Late Years: 1943-1968
Dehn’s romance with Elizabeth Timmerman seems to have floundered in the early 1940s, but in 1943 he met a beautiful young woman, Virginia Engelman, twenty-three years his junior, who was working in the print department of Associated American Artists. After four years of courtship, he married her in 1947, and at that point entered into the final phase of his career—one marked by considerable financial success and domestic harmony. By this time “realist” artists such as Dehn were being pushed out of the spotlight in the New York art world by the rise of Abstract Expressionism and other radical modern styles. Nonetheless, during this period Dehn probably achieved the peak of his national fame and financial success with his prints and watercolors, many of them celebrating exotic or tropical locales such as Cuba, Haiti, the Yucatan, Italy Greece, Turkey, Iran, Afghanistan and India. About every other year he would schedule several weeks of intense works the Desjobert lithography shops in Paris, where he continued to experiment with new techniques, including his first color prints. Some of Dehn’s most popular work was produced during this period, including a watercolor titled Spring in Central Park, owned by the Metropolitan Museum of Art, which has been widely reproduced on everything from calendars and handbags—and rivals the most famous works in the collection in its popularity. During this period he continued to work at a frantic pace, although he suffered from a series of health problems, including hypertension and insomnia. The end came suddenly. On May 19, 1968, while organizing prints in his field, he suffered a massive heart attack. At the time two major projects were already in the works to celebrate his career: a book of his drawings, published by the University of Missouri Press, and a retrospective exhibition of his work organized by Mahonri Sharp Young at the Columbus Gallery of Fine Arts in Columbus, Ohio.
Dehn’s Place in the History of Art
Where does Dehn stand in the history of art? While he never did much in oil painting, in printmaking and watercolor he ranks nearly on a par with the very greatest American masters of this medium. His lithographs of the ‘twenties, with their frank depiction of nightclubs, with their performers, prostitutes, and portly patrons, introduced a new note of social satire into American printmaking; and he was one of the most gifted printmakers of the American Scene movement of the 1930s, nearly on a rank with figures such as Thomas Hart Benton and Grant Wood. Undoubtedly the most unique quality of Dehn’s work was his extraordinary exploration of new textures and techniques, which moves lithography away from mere crayon drawing into a new creative realm.
In his day, Dehn was widely regarded as one of the greatest of contemporary lithographers. Indeed, by the time of his death Dehn’s work was represented in the collections of over fifty major art museums in both Europe and the United States, including the Metropolitan Museum of Art; the Whitney Museum of American Art, the Museum of Fine Arts, Boston; The Brooklyn Museum,; the Minneapolis Institute of Fine Arts; the New York Public Library; the British Museum; the Kupferstick Kabinet in Berlin; and the Albertina in Vienna.
“Few artists have ever made the lithographic stone work as Dehn has, got so much richness out of it, so large a range of color, so tremendously sensuous an effect” wrote Guy Pene DuBois in Creative Art. “The scope of lithography seems to have been enlarged, thanks to his artist, by many leagues,” wrote Edward Alden Jewell in The New York Times.
Clinton Adams, who wrote the major book on American lithography, noted that Dehn had an extraordinary influence on his fellow artists. As Virginia Dehn recalled:
Adams told me at lunch the other day that Adolf worked with many printers that his artistic influence was very widespread. As a result of working with new litho techniques Adolf devised they were able to go ahead and suggest the techniques to other artists they worked with.
In a rather similar fashion, his watercolors rank with the best produced in American art of their period, and are also notable for their lively range of subject matter and highly creative use of new techniques.
For Dehn himself, art was primarily a way of connecting with life. Virginia Dehn recalled:
“He never made statements about his greatest contributions as an artist. He was essentially a modest man. Nor did he ever to my knowledge say that that he was a stronger technician than anyone else. He did have, I think, a quite belief in his achievements in lithography and watercolor.”
When asked late in life to produce a statement for a show of his work at St. Olaf College, in Northfield, Minnesota, Dehn chose to produce a sort of anti-statement—a plea that art is something that shouldn’t be reduced to an explanation. Along the way he slipped in a few digs at the abstract crowd, who he felt had reduced art to something to puzzle over rather than to enjoy. As he wrote:
You ask for a statement concerning my work. So my statement is a statement against making a statement. My paintings are my statement. What I have to offer as a painter is direct and simple and words are not necessary to a greater understanding or enjoyment of them. If anyone does not understand then words will not help him. I cannot imagine El Greco or Rembrandt or Renoir being asked for a statement every time they showed a painting, or if they were asked troubling to write one. Let us leave such statement, which are often grandiloquent, high sounding and ambiguous to the avant-garde boys who make them. Their paintings bewilder the dear pubic whom we all want to educate and their statements only add to the befuddlement.
Surely Dehn’s central goal was not to change the history of art, but to provide a sort of living record of the life he lived, and to give delight to the viewer. He once declared that “the very act of drawing made me participate in the life around me,” and as he once wrote:
“My attitude to life is rather sensuous—and sensual too—and only after I have filled myself with sensuous experiences can I go about working. Putting it simply: when I am fed up, I work. I am crazy about life and want to have as much out of it as I can. Take away my work and I lose interest in life, yet the work comes after my living life, or rather out of it.”
Looking at his work--even at the satires which have an element of the gothic and morbid
-- it is hard not to feel delight both in the work itself and in one’s sense of a life well lived.
- Creator:Adolf Dehn (1895 - 1968, American)
- Creation Year:1930
- Dimensions:Height: 19.125 in (48.58 cm)Width: 13.5 in (34.29 cm)
- Medium:
- Movement & Style:
- Period:
- Condition:
- Gallery Location:Fairlawn, OH
- Reference Number:
About the Seller
5.0
Recognized Seller
These prestigious sellers are industry leaders and represent the highest echelon for item quality and design.
Platinum Seller
These expertly vetted sellers are 1stDibs' most experienced sellers and are rated highest by our customers.
Established in 1978
1stDibs seller since 2013
718 sales on 1stDibs
Typical response time: 1 hour
Associations
International Fine Print Dealers Association
- ShippingRetrieving quote...Ships From: Fairlawn, OH
- Return PolicyA return for this item may be initiated within 10 days of delivery.
More From This SellerView All
- Trout Fishing on the Gunnison (Colorado)By Adolf DehnLocated in Fairlawn, OHTrout Fishing on the Gunnison (Colorado) Lithograph, 1941 Signed and dated '42 in pencil lower right Annotated lower left: "40 Prints-The Gunnison River, Colorado-For Anne & Jack" Ed...Category
1940s American Modern Landscape Prints
MaterialsLithograph
- Niagara FallsBy Adolf Arthur DehnLocated in Fairlawn, OHNiagara Falls Lithograph, 1931 Signed lower right (see photo) Titled/edition lower left. (see photo) Edition of 25 Provenance: the Estate of the Artist Condition: Excellent Image si...Category
1930s American Modern Landscape Prints
MaterialsLithograph
- Boulder DamBy Adolf DehnLocated in Fairlawn, OHBoulder Dam Lithograph, 1946 Signed and dated in pencil lower right (see photo) Titled in pencil lower left (see photo) Printed by Lawrence Barrett, Colorado Springs Edition of 40 or...Category
1940s American Modern Landscape Prints
MaterialsLithograph
- Brooklyn WaterfrontBy Adolf Arthur DehnLocated in Fairlawn, OHBrooklyn Waterfront Lithograph, 1931 Signed, titled, and dated in pencil by the artist Edition: Undetermined (very small), plus artist's proofs Printed by Meister Schulz, Berlin Provenance: Estate of the artist Virginia Dehn, the artist's widow Dehn Quests Bibliography: Lumsdaine and O'Sullivan 152 Illustrated: Adams, The Sensuous Life of Adolf Dehn, Fig. 9.14, page 213 (This impression) Adolf Dehn, American Watercolorist and Printmaker, 1895-1968 Adolf Dehn was an artist who achieved extraordinary artistic heights, but in a very particular artistic sphere—not so much in oil painting as in watercolor and lithography. Long recognized as a master by serious print collectors, he is gradually gaining recognition as a notable and influential figure in the overall history of American art. In the 19th century, with the invention of the rotary press, which made possible enormous print runs, and the development of the popular, mass-market magazines, newspaper and magazine illustration developed into an artistic realm of its own, often surprisingly divorced from the world of museums and art exhibitions, and today remains surprisingly overlooked by most art historians. Dehn in many regards was an outgrowth of this world, although in an unusual way, since as a young man he produced most of his illustrative work not for popular magazines, such as The Saturday Evening Post, but rather for radical journals, such as The Masses or The Liberator, or artistic “little magazines” such as The Dial. This background established the foundation of his outlook, and led later to his unique and distinctive contribution to American graphic art. If there’s a distinctive quality to his work, it was his skill in introducing unusual tonal and textural effects into his work, particularly in printmaking but also in watercolor. Jackson Pollock seems to have been one of many notable artists who were influenced by his techniques. Early Years, 1895-1922 For an artist largely remembered for scenes of Vienna and Paris, Adolf Dehn’s background was a surprising one. Born in Waterville, Minnesota, on November 22, 1895, Dehn was the descendent of farmers who had emigrated from Germany and homesteaded in the region, initially in a one-room log cabin with a dirt floor. Adolf’s father, Arthur Clark Dehn, was a hunter and trapper who took pride that he had no boss but himself, and who had little use for art. Indeed, during Adolf’s boyhood the walls of his bedroom and the space under his bed were filled with the pelts of mink, muskrats and skunks that his father had killed, skinned and stretched on drying boards. It was Adolf’s mother, Emilie Haas Dehn, a faithful member of the German Lutheran Evangelical Church, who encouraged his interest in art, which became apparent early in childhood. Both parents were ardent socialists, and supporters of Eugene Debs. In many ways Dehn’s later artistic achievement was clearly a reaction against the grinding rural poverty of his childhood. After graduating from high school in 1914 at the age of 19—an age not unusual in farming communities at the time, where school attendance was often irregular—Dehn attended the Minneapolis School of Art from 1914 to 1917, whose character followed strongly reflected that of its director, Munich-trained Robert Kohler, an artistic conservative but a social radical. There Dehn joined a group of students who went on to nationally significant careers, including Wanda Gag (later author of best-selling children’s books); John Flanagan (a sculptor notable for his use of direct carving) Harry Gottlieb (a notable social realist and member of the Woodstock Art Colony), Elizabeth Olds (a printmaker and administrator for the WPA), Arnold Blanch (landscape, still-life and figure painter, and member of the Woodstock group), Lucille Lunquist, later Lucille Blanch (also a gifted painter and founder of the Woodstock art colony), and Johan Egilrud (who stayed in Minneapolis and became a journalist and poet). Adolf became particularly close to Wanda Gag (1893-1946), with whom he established an intense but platonic relationship. Two years older than he, Gag was the daughter of a Bohemian artist and decorator, Anton Gag, who had died in 1908. After her husband died, Wanda’s mother, Lizzi Gag, became a helpless invalid, so Wanda was entrusted with the task of raising and financially supporting her six younger siblings. This endowed her with toughness and an independent streak, but nonetheless, when she met Dehn, Wanda was Victorian and conventional in her artistic taste and social values. Dehn was more socially radical, and introduced her to radical ideas about politics and free love, as well as to socialist publications such as The Masses and The Appeal to Reason. Never very interested in oil painting, in Minneapolis Dehn focused on caricature and illustration--often of a humorous or politically radical character. In 1917 both Dehn and Wanda won scholarships to attend the Art Students League, and consequently, in the fall of that year both moved to New York. Dehn’s art education, however, ended in the summer of 1918, shortly after the United States entered World War I, when he was drafted to serve in the U. S. Army. Unwilling to fight, he applied for status as a conscientious objector, but was first imprisoned, then segregated in semi-imprisonment with other Pacifists, until the war ended. The abuse he suffered at this time may well explain his later withdrawal from taking political stands or making art of an overtly political nature. After his release from the army, Dehn returned to New York where he fell under the spell of the radical cartoonist Boardman Robinson and produced his first lithographs. He also finally consummated his sexual relationship with Wanda Gag. The Years in Europe: 1922-1929 In September of 1921, however, he abruptly departed for Europe, arriving in Paris and then moving on to Vienna. There in the winter of 1922 he fell in love with a Russian dancer, Mura Zipperovitch, ending his seven-year relationship with Wanda Gag. He and Mura were married in 1926. It was also in Vienna that he produced his first notable artistic work. Influenced by European artists such as Jules Pascin and Georg Grosz, Dehn began producing drawings of people in cafes, streets, and parks, which while mostly executed in his studio, were based on spontaneous life studies and have an expressive, sometimes almost childishly wandering quality of line. The mixture of sophistication and naiveté in these drawings was new to American audiences, as was the raciness of their subject matter, which often featured pleasure-seekers, prostitutes or scenes of sexual dalliance, presented with a strong element of caricature. Some of these drawings contain an element of social criticism, reminiscent of that found in the work of George Grosz, although Dehn’s work tended to focus on humorous commentary rather than savagely attacking his subjects or making a partisan political statement. Many Americans, including some who had originally been supporters of Dehn such as Boardman Robinson, were shocked by these European drawings, although George Grocz (who became a friend of the artist in this period) admired them, and recognized that Dehn could also bring a new vision to America subject matter. As he told Dehn: “You will do things in America which haven’t been done, which need to be done, which only you can do—as far at least as I know America.” A key factor in Dehn’s artistic evolution at this time was his association with Scofield Thayer, the publisher of the most notable modernist art and poetry magazine...Category
1920s American Modern Landscape Prints
MaterialsLithograph
- Central Park NightBy Adolf DehnLocated in Fairlawn, OHCentral Park Night Lithograph, 1946 Signed and dated lower right (see photo) Titled, lower center Number lower left (see photo) Edition: 40, plus trial proofs (23/40) This image depi...Category
1940s American Modern Landscape Prints
MaterialsLithograph
- St. George Hotel SearchlightBy Adolf DehnLocated in Fairlawn, OHSt. George Hotel Searchlight Lithograph, 1930 Signed in pencil lower right (see photo) Titled lower left (see photo) Edition: 30 Printed by Meister Schulz, Berlin The image depicts t...Category
1930s American Modern Landscape Prints
MaterialsLithograph
You May Also Like
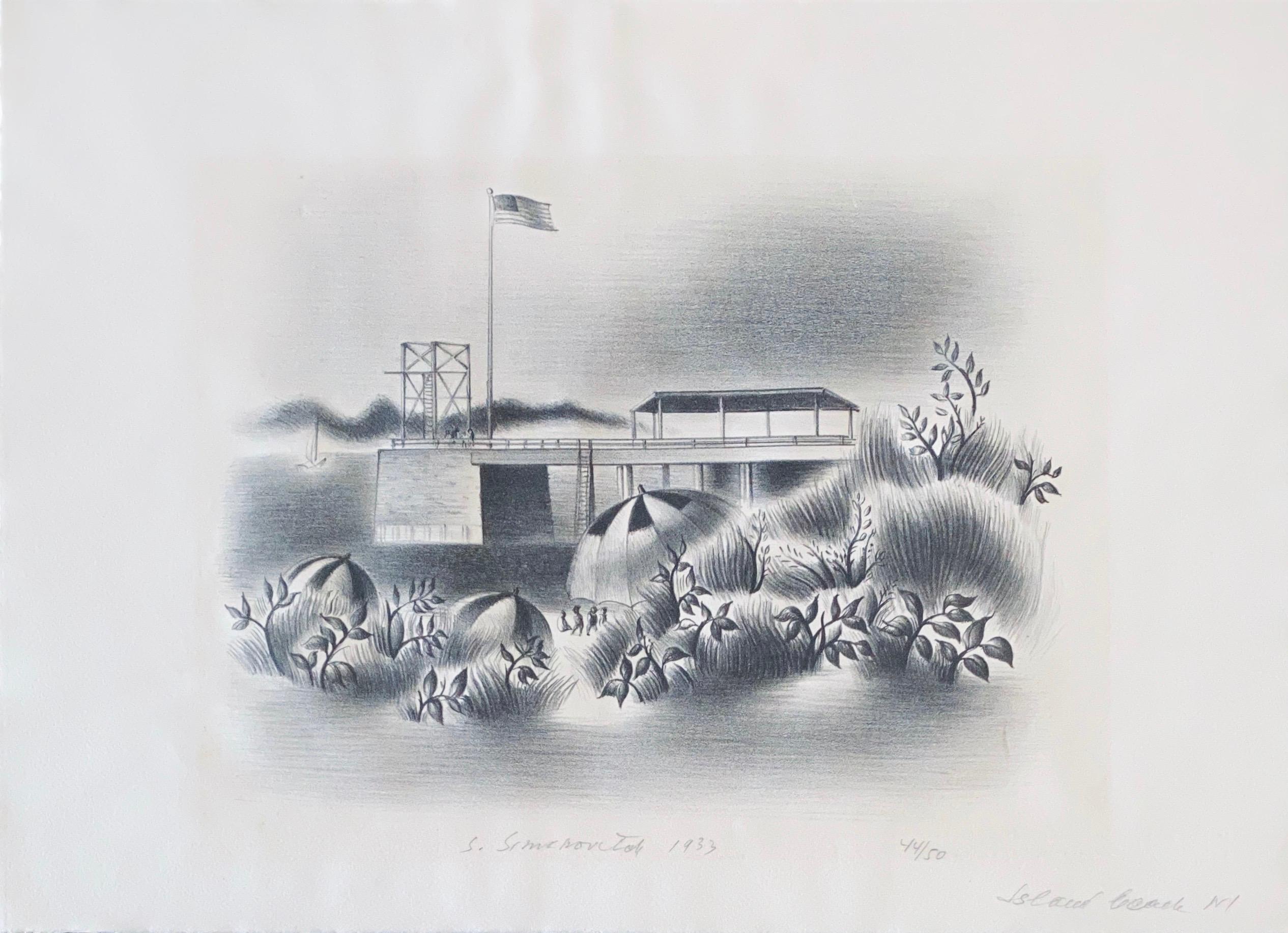
- Simka Simkhovitch WPA Artist Lithograph Island Beach 1933 American ModernistBy Simka SimkhovitchLocated in Surfside, FLSimka Simkhovitch (Russian/American 1893 - 1949) signed lithograph. Pencil signed and dated "S. Simkhovitch 1933" lower center. Title "Island Beach," in pencil lower left of sheet. Numbered "44/50" in pencil lower right. (it is either Island Beach Wisconsin or New Jersey) Simka Simkhovitch (Симха Файбусович Симхович) (aka Simka Faibusovich Simkhovich) (Novozybkov, Russia May 21, 1885 O.S./June 2, 1885 N.S.—Greenwich, Connecticut February 25, 1949) was a Ukrainian-Russian Jewish artist and immigrant to the United States. He painted theater scenery in his early career and then had several showings in galleries in New York City. Winning Works Progress Administration (WPA) commissions in the 1930s, he completed murals for the post offices in Jackson, Mississippi and Beaufort, North Carolina. His works are in the permanent collections of the Dallas Museum of Art, the National Museum of American Art and the Whitney Museum of American Art. Born outside Kyiv (Petrograd Ukraine) into a Jewish family who owned a small department store. During a severe case of measles when he was seven, Simcha Simchovitch sketched the views outside his window and decided to become an artist, over his father's objections. Beginning in 1905, he studied at the Grekov Odessa Art School and upon completion of his studies in 1911 received a recommendation to be admitted to the Imperial Academy of Arts. Though he enrolled to begin classes in architecture, painting, and sculpture at the Imperial Academy, he was dropped from the school roster in December because of the quota on the number of Jewish students and drafted into the army. Simchovitch served as a private in the 175th Infantry Regiment Baturyn [ru] until his demobilization in 1912. Re-enrolling in the Imperial Academy, he audited classes. Simka Simkhovitch exhibited paintings and sculptures in 1918 as part of an exhibition of Jewish artists and in 1919 placed 1st in the competition "The Great Russian Revolution" with a painting called "Russian Revolution" which was hung in the State Museum of Revolution. In 1922, Simkha Simkhovitch exhibited at the International Book Fair in Florence (Italian: Fiera Internazionale del Libro di Firenze). In 1924, Simkhovitch came to the United States to make illustrations for Soviet textbooks and decided to immigrate instead. Initially he supported himself by doing commercial art and a few portrait commissions. In 1927, he was hired to paint a screen for a scene in the play "The Command to Love" by Fritz Gottwald and Rudolph Lothar which was playing at the Longacre Theatre on Broadway. Art dealers began clamoring for the screen and Simkhovitch began a career as a screen painter for the theater. Catching the attention of the screenwriter, Ernest Pascal, he worked as an illustrator for Pascal, who then introduced him to gallery owner, Marie Sterner. Simkhovitch's works appeared at the Marie Sterner Gallery beginning with a 1927 exhibit and were repeated the following year. Simkhovitch had an exhibit in 1929 at Sterner's on circus paintings. In 1931, he held a showing of works at the Helen Hackett Gallery, in New York City and later that same year he was one of the featured artists of a special exhibit in San Francisco at the California Palace of the Legion of Honor in Lincoln Park. The exhibit was coordinated by Marie Sterner and included four watercolors, including one titled "Nudes". He is of the generation of Russian Soviet artists such as Isaac Pailes, Serge Charchoune, Marc Chagall, Chana Orloff, Isaac Ilyich Levitan, and Ossip Zadkine. In 1936, Simkhovitch was selected to complete the mural for the WPA Post office project in Jackson, Mississippi. The mural was hung in the post office and courthouse in 1938 depicted a plantation theme. Painted on the wall behind the judge’s bench, “Pursuits of Life in Mississippi”, a depiction of black workers engaged in manual labor amid scenes of white professionals and socialites, was eventually covered over in later years during renovations due to its stereotypical African American imagery. The following year, his painting "Holiday" won praise at an exhibition in Lincoln, Nebraska. In 1940, Simkhovitch's second WPA post office project was completed when four murals, "The Cape Lookout Lighthouse and the Orville W. Mail Boat", "The Wreck of the Crissie Wright", "Sand Ponies" and "Canada Geese" were installed in Beaufort, North Carolina. The works were commissioned in 1938 and did not generate the controversy that the Jackson mural had. The main mural is "The Wreck of the Crissie Wright" and depicts a shipwreck which had occurred in Beaufort in 1866. "The Cape Lookout Lighthouse and the Orville W. Mail Boat" depicted the lighthouse built in 1859 and the mail boat that was running mail during the time which Simkhovitch was there. The boat ran mail for the area until 1957. "Sand Ponies" shows the wild horses common to the North Carolina barrier islands and "Canada Geese" showed the importance of hunting and fishing in the area. All four murals were restored in the 1990s by Elisabeth Speight, daughter of two other WPA muralists, Francis Speight...Category
1930s American Modern Landscape Prints
MaterialsLithograph
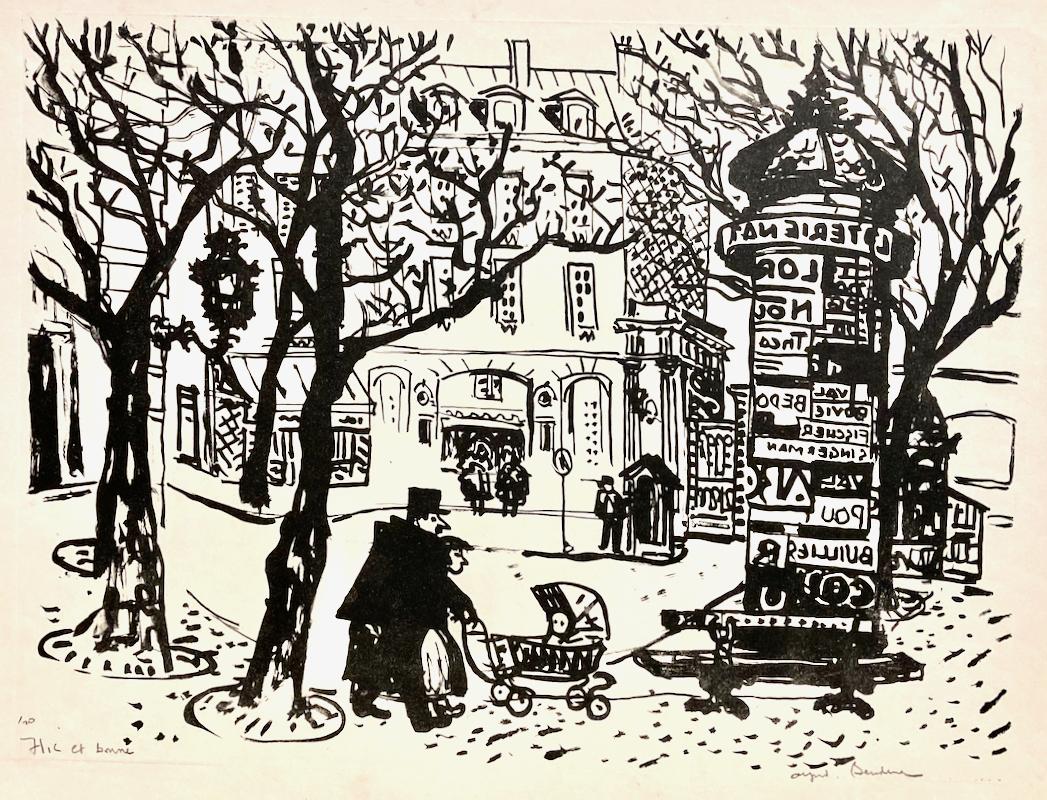
- Alfred Bendiner, Flic et Bonne (Gendarme and Nursemaid)By Alfred BendinerLocated in New York, NYThe world was Bendiner's oyster, but here he shows us a all we need in a small corner of Paris. It's charming and safe: the 'Flic et Bonne' (gendarme and nursemaid) are together, goi...Category
1950s American Modern Landscape Prints
MaterialsLithograph
- Alfred Bendiner, Rue des Matrys (Paris)By Alfred BendinerLocated in New York, NYWorld traveler that he was, Bendiner was clearly at home in Paris. He found everyone fascinating and has made this print a compendium of local characters and types. Nothing escapes h...Category
1950s American Modern Landscape Prints
MaterialsLithograph
- Alfred Bendiner, Place St. Andre des Arts (Paris)By Alfred BendinerLocated in New York, NYThe Place St. Andre des Arts, on the Left Bank in Paris, would have been a natural environment for Bendiner. It was the Latin Quarter, just south of the Louvre and near everything im...Category
1950s American Modern Landscape Prints
MaterialsLithograph
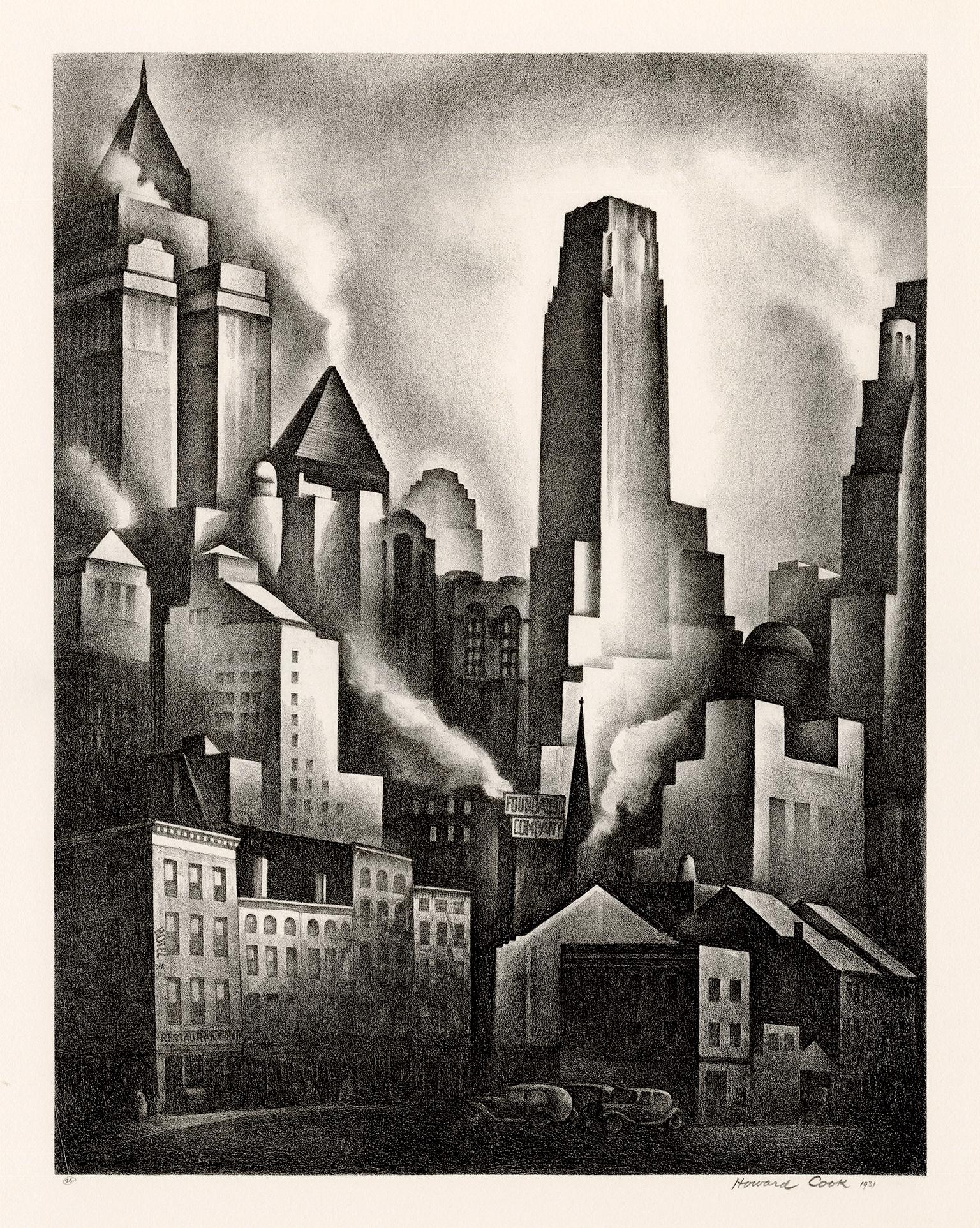
- 'Financial District', New York City — 1930s American ModernismBy Howard Norton CookLocated in Myrtle Beach, SCHoward Cook, 'Financial District', lithograph, 1931, edition 75, Duffy 155. A fine, richly-inked impression, on cream wove paper, the full sheet with wide margins (2 3/4 to 5 5/8 inches), in excellent condition. Image size 13 5/16 x 10 3/8 inches (338 x 264 mm); sheet size 23 x 16 inches (584 x 406 mm). Matted to museum standards, unframed. Literature: 'American Master Prints from the Betty and Douglas Duffy Collection', the Trust for Museum Exhibitions, Washington, D.C., 1987. Collections: Crystal Bridges Museum of American Art, Library of Congress, Metropolitan Museum of Art, Philadelphia Museum of Art, Smithsonian American Art Museum. ABOUT THE ARTIST Howard Norton Cook (1901-1980) was one of the best-known of the second generation of artists who moved to Taos. A native of Massachusetts, he studied at the Art Students League in New York City and at the Woodstock Art Colony. Beginning his association with Taos in 1926, he became a resident of the community in the 1930s. During his career, he received two Guggenheim Fellowships and was elected an Academician in the National Academy of Design. He earned a national reputation as a painter, muralist, and printmaker. Cook’s work in the print mediums received acclaim early in his career with one-person exhibitions at the Denver Art Museum (1927) and the Museum of New Mexico (1928). He received numerous honors and awards over the years, including selection in best-of-the-year exhibitions sponsored by the American Institute of Graphics Arts, the Brooklyn Museum, the Society of American Etchers, and the Philadelphia Print Club. His first Guggenheim Fellowship took him to Taxco, Mexico in 1932 and 1933; his second in the following year enabled him to travel through the American South and Southwest. Cook painted murals for the Public Works of Art Project in 1933 and the Treasury Departments Art Program in 1935. The latter project, completed in Pittsburgh, received a Gold Medal from the Architectural League of New York. One of his most acclaimed commissions was a mural in the San Antonio Post Office in 1937. He and Barbara Latham settled in Talpa, south of Taos, in 1938 and remained there for over three decades. Cook volunteered in World War II as an Artist War Correspondent for the US Navy, where he was deployed in the Pacific. In 1943 he was appointed Leader of a War Art Unit...Category
1930s American Modern Figurative Prints
MaterialsLithograph
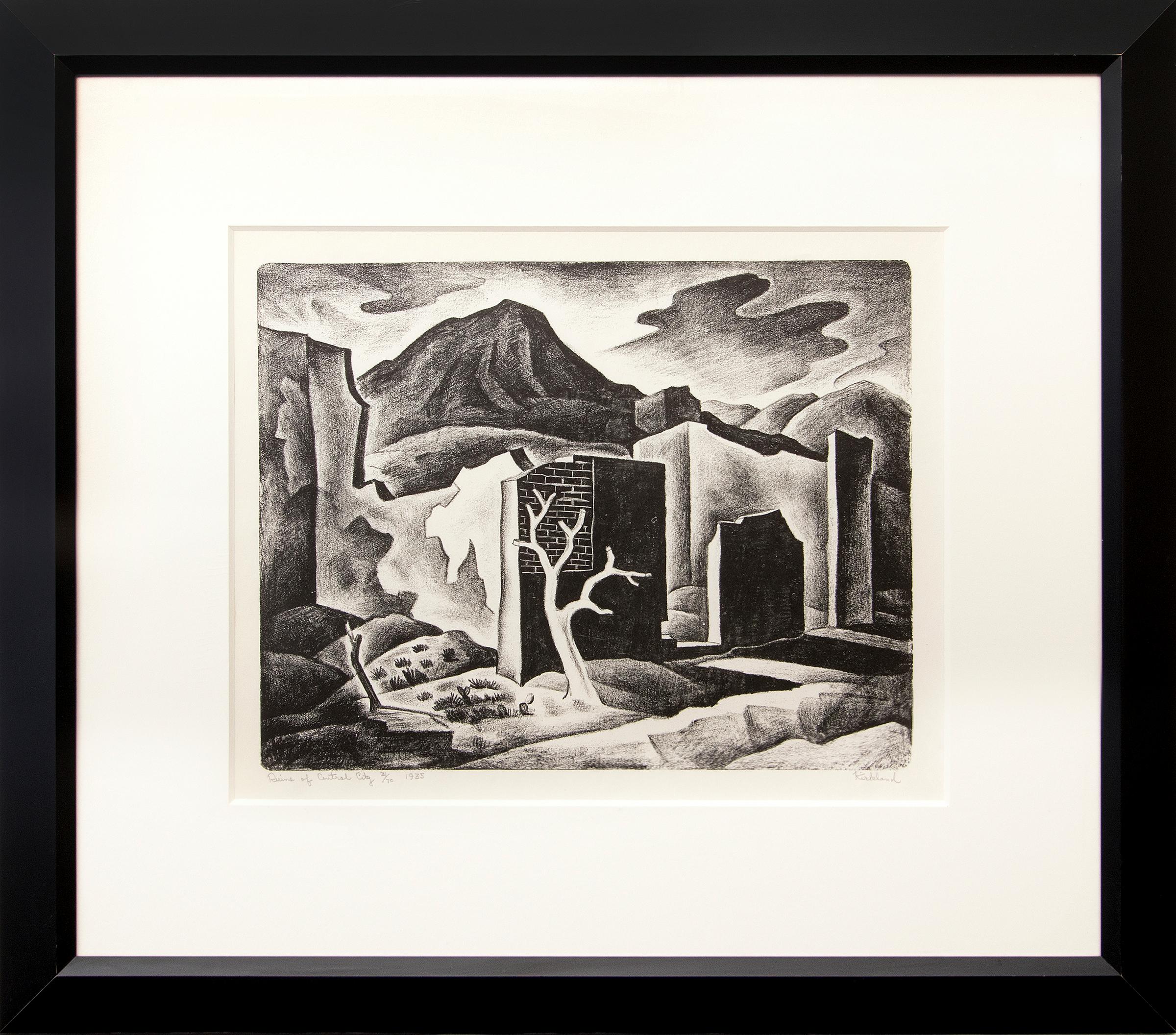
- Ruins of Central City, Vintage 1935 Framed Colorado Modernist LandscapeBy Vance KirklandLocated in Denver, COVintage lithograph titled "Ruins of Central City 31/70" is a modernist landscape with decaying buildings and mountains by Vance Hall Kirkland, from 1935. Presented in a custom black frame with archival materials, outer dimensions measure 25 ⅞ x 29 ⅜ x ⅝ inches. Image sight size is 14 x 17 ¾ inches. Painting is clean and in very good vintage condition - please contact us for a detailed condition report. Provenance: Private collection, Denver, Colorado Expedited and international shipping is available - please contact us for a quote. About the Artist: Variously referred to as the "Father of Modern Colorado Painting", "Dean of Colorado Artists", and "Colorado’s pre-eminent artist," Kirkland was an inventive, visionary painter who spent fifty-two years of his fifty-four-year career in Denver. Of the approximately 1,200 paintings he created, about 550 from the first half of his career (1927-1953) are water-based media: acquarelle, gouache, casein and egg tempera, with a few oils. In the latter half of his career (1953-1981) he used oil and his unique oil and water mixture. He also produced five hundred drawings and some ten prints, mostly lithographs on stone, while also engaged in teaching full-time for most of the period. To show people "something they have never seen before and new ways to look at things," he felt he needed to preserve his artistic freedom. Consequently, he chose to spend his entire professional career in Denver far removed from the established American art centers in the East and Midwest. "By minding my own business and working on my own," he said, "I think it was possible to develop in this part of the country… I’ve developed my kind of work [and] I think my paintings are stronger for having worked that way." The geographical isolation resulting from his choice to stay in Colorado did not impede his creativity, as it did other artists, but in fact contributed to his unique vision. The son of a dentist, who was disappointed with his [son’s] choice of art as a career, Kirkland flunked freshman watercolor class in 1924 at the Cleveland School of Art (now the Cleveland Institute of Art) for putting colors into his landscapes that did not exist in nature and for competing colors. Not dissuaded, he won first prize for his watercolors in his junior and senior years. [While in Cleveland,] he studied with three influential teachers. Henry Keller, included in the prestigious New York Armory Show in 1913, introduced him to designed realism which he later used in his Colorado landscapes in the 1930s and 1940s. His other teachers were Bill Eastman, who studied with Hans Hofmann and appreciated all the new movements in modern art, and Frank Wilcox, a fine watercolorist. While a student at the Cleveland School of Art, Kirkland concurrently took liberal arts courses at Western Reserve and the Cleveland School of Education and taught two freshman courses in watercolor and design, receiving his diploma in painting from the school in 1927 by doing four years of work in three. The following year he received a Bachelor of Education in Art degree from the same institution. In 1929 he assumed the position of founding director of the University of Denver’s School of Art, originally known as the Chappell School of Art. He resigned three years later when the university reneged on its agreement to grant its art courses full recognition toward a Bachelor of Arts degree. His students prevailed on him to continue teaching, resulting in the Kirkland School of Art which he opened in 1932 at 1311 Pearl Street in Denver. The building, where he painted until his death in 1981, formerly was the studio of British-born artist, Henry Read, designer of the City of Denver Seal and one of the original thirteen charter members of the Artists’ Club of Denver, forerunner of the Denver Art Museum. The Kirkland School of Art prospered for the next fourteen years with its courses accredited by the University of Colorado Extension Center in Denver. The teaching income from his art school and his painting commissions helped him survive the Great Depression. The U.S. Treasury Department’s Section of Fine Arts commissioned from him two post office murals, Cattle Roundup (1938, Eureka, Kansas), and Land Rush (1940, Sayre, Oklahoma). He also did murals for several Denver clients: the Gerald Hughes mansion (1936, later demolished), Arthur Johnson home (1936-37, Seven Drinks of Man), Albany Hotel (1937, later demolished), Neustetter’s Department Store (1937, "History of Costume," three of five saved in 1987 before the building interior was demolished in advance of its condo conversion), and the Denver Country Club (1945, partially destroyed and later painted over). In 1953 the Ford Times, published by the Ford Motor Company, commissioned Kirkland along with fellow Denver artists, William Sanderson and Richard Sorby, to paint six watercolors each for the publication. Their work appeared in articles [about] Colorado entitled, "Take to the High Road" (of the Colorado Rockies) by Alicita and Warren Hamilton. Kirkland sketched the mountain passes and high roads in the area of Mount Evans, Independence Pass near Aspen, and Trail Ridge Road in Rocky Mountain National Park. In 1946 Kirkland closed his art school when the University of Denver rehired him as director of its School of Art and chairman of the Division of Arts and Humanities. In 1957 the University gave him its highest honor – the "University Lecturer Award." When he retired in 1969 as Professor of Art Emeritus to become a full-time painter, the School of Arts was the university’s largest undergraduate department. In 1971 Governor John Love presented Kirkland the State of Colorado Arts and Humanities Award. In addition to his dual positions as artist and teacher in Denver for more than half a century, he served the Denver Art Museum as a trustee, chairman of the accessions committee, member of the exhibitions committee, curator of European and American art, and honorary curator of painting and sculpture. He also won the battle with the museum’s old guard to establish a department of modern and contemporary art. Additionally, he was one of the fifty-two founding members of the Denver Artists Guild which included most of Colorado’s leading artists who greatly contributed to the state’s cultural history. Kirkland developed five major painting periods during his life encompassing various series with some chronological overlap: Designed Realism (1927-1944); Surrealism (1939-1954); Hard Edge Abstraction, including the Timberline Abstraction Series (1947-1957); Abstract Expressionism with four series – Nebulae, Roman, Asian, and Pure Abstractions (1951-1964); and the Dot Paintings with five series – Energy of Vibrations, Mysteries, Explosions, Forces, and Pure Abstractions (1963-1981). Nevadaville (1931), a watercolor, belongs to Kirkland’s initial period of Designed Realism. Adapting nature by redesigning the realism he saw on location in Colorado allowed him to be "more concerned with the importance of the painting rather than the importance of the landscape." He noted that the rhythms his Cleveland teacher, Henry Keller, "found in nature created a certain movement in his paintings… [that moved] away from the static element of a lot of realistic, representational painting." Kirkland, along with fellow watercolorist Elisabeth Spalding, were some of the first Denver artists interesting themselves in Colorado’s nineteenth-century mining towns west of Denver. They offered an alternative to the overwrought cowboy and Indian subject matter of the previous generation; while the human and architectural components of the mining towns provided a welcome break from the predominant nineteenth-century landscape tradition. Vibrations of Two Yellows in Space (1970), one of Kirkland’s small subseries of "Open Sun Paintings," occupies the final phase in his first series of dot paintings, Energy of Vibrations in Space (1963-1972). Many pieces in the series incorporate his unique mixture of oil paint and water which he developed in the early 1950s. The work in the subseries – a challenge to the viewer’s optic nerve – constitutes his contribution to the international realm of Op Art. Recalling the theory of pulsating galaxies and the universe, he used dots applied with dowels of different sizes to surround and leave round open spaces letting the gradient background show through. Because of the color contrast between the two, the "suns" either recede into the background or jump out in the foreground, creating the powerful pulsing effect. During his lifetime he assembled on a limited budget an extensive collection of fine and decorative art and furniture. His collecting passion dated from his student days when he used his prize money from the Cleveland School of Art to purchase a watercolor by William Eastman and a now-famous set of Russian musician figures by Alexander Blazys, both of whom were his professors. After Kirkland’s death, the Denver Art Museum received a large bequest that included paintings by Roberto Matta, Gene Davis, Charles Burchfield, and Richard Anuszkiewicz (the two latter-named also alumni of the Cleveland Institute of Art); prints by Arthur B. Davies, Roberto Matta, Pablo Picasso, and Robert Rauschenberg; and a sculpture by Ossip Zadkine. Kirkland posthumously was the subject of a television documentary, "Vance Kirkland’s Visual Language," aired on over one hundred PBS television stations (1994-96), and in 1999 a six-scene biographical ballet choreographed by Martin Friedmann with scenario provided by Hugh Grant, founder and director of the Kirkland Museum of Fine & Decorative Art in Denver. Historic Denver also posthumously honored Kirkland as part of the Colorado 100. From 1997 to 2000 Kirkland’s solo exhibition was hosted by thirteen European museums: Fondazione Muduma, Milan; Sala Parpalló Museum Complex, València; Stadtmuseum, Düsseldorf; Frankfurter Kunstverein; Museum of Modern Art, Vienna; Kiscelli Múzeum and the Museum of Fine Arts, Budapest; Czech Museum of Fine Arts, Prague; National Museum, Warsaw; State Gallery of the Art of Poland, Sopot/Gdańsk, National Museum of Art, Kaunas, Lithuania; Latvian Foreign Art Museum, Riga; and the State Russian Museum, St. Petersburg. Solo Exhibitions: Denver Art Museum (1930, 1935, 1939-40, 1942, 1972, 1978-retrospective, 1988, 1998); Colorado Springs Fine Arts Center (1943); Knoedler & Company, New York (1946, 1948, 1952); Pogzeba Art Gallery, Denver (1959); Galleria Schneider, Rome (1960); Birger Sandzén Memorial Gallery, Lindsborg, Kansas (1964-65,1977); Genesis Galleries, Ltd., New York (1978); Valhalla Gallery, Wichita, Kansas (1979); Inkfish Gallery, Denver (1980); Colorado State University, Fort Collins (1981- memorial exhibition); Boulder Center for the Visual Arts (1985); University of Denver, Schwayder Art Gallery (1991). Group Exhibitions (selected): "May Show," Cleveland Museum of Art (1927-28); "Western Annuals," Denver Art Museum (1929-1957, 1964, 1966, 1968, 1971); "International Exhibition of Watercolors, Pastels, Drawings and Monotypes," Art Institute of Chicago (1930-1946); "Abstract and Surrealist American Art," Art Institute of Chicago (1947-48, traveled to ten other American museums); "Midwest Artists Exhibition," Kansas City Art Institute (1932, 1937, 1939-1942); Dallas Museum of Art (1933, 1960); San Diego Museum of Art (1941); "Artists for Victory," Metropolitan Museum of Art (1942); "United Nations Artists in America," Argent Galleries, New York (1943); "California Watercolor Society," Los Angeles County Museum (1943-1945); "Survey of Romantic Painting," Museum of Modern Art, New York (1945); New Mexico Museum of Art, Santa Fe (1945, 1951); Knoedler & Company, New York (1946-57; co-show with Max Ernest, 1950; co-show with Bernard Buffet, 1952); Joslyn Art Museum, Omaha (1948, 1956); Philbrook Art Center, Tulsa, Oklahoma (1951); "Contemporary American Painting," University of Illinois, Urbana (1952); University of Utah, Salt Lake (1952-53); Oakland Art Museum (1954-55); "Reality and Fantasy, 1900-54," Walker Art Center, Minneapolis (1954); "Art U.S.A.," Madison Square Garden, New York (1958); Roswell Museum and Art Center, New Mexico (1961); Burpee Art Museum, Rockford, Illinois (1965-68); University of Arizona Art...Category
1930s American Modern Landscape Prints
MaterialsPaper, Lithograph
Recently Viewed
View AllMore Ways To Browse
New York Vintage Shops
1950s New Look
Victorian New York
Secretary New
American Secretary
Night In Venice
Venice At Night
Beige Dial
New Art Wares
Wood Landscape Carvings
Large Tropical Prints
19th Century American Politics
Book Of Spells
1930s Wpa Prints
1930 Secretary
1930s Fashion Drawing
June Felter
Landscape Watercolor Tropical